_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
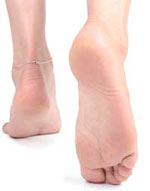
New research concludes that acupuncture is effective for treating plantar fasciitis, a painful inflammatory foot condition. Plantar fasciitis typically presents with pain on the underside of the foot and heel. The pain is often most severe when first stepping out of bed onto the floor in the morning. Another telltale sign of plantar fasciitis is pain upon dorsiflexion, lifting the foot towards the shin.
 HealthCMi News
HealthCMi News In this controlled clinical investigation, the acupuncture group demonstrated a significant reduction in foot pain while the control group showed only minimal changes. The control group received five weeks of analgesic medications, stretching exercises and shoe modifications. The acupuncture group received the same therapies plus electro-acupuncture treatments. The researchers concluded that, “Electro-acupuncture coupled with conventional treatments provided a success rate of 80% in chronic planar fasciitis which was more effective than conventional treatments alone.”
Another recent study demonstrates that acupuncture is effective for the treatment of plantar heel pain. The researchers note that acupuncture has more significant improvements in both pain relief and the restoration of function than a standard regime of care that includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications. Based on these findings, the researchers formally recommend acupuncture for the treatment of plantar heel pain.
In yet another study, investigators concluded that acupuncture at acupoint P7 (Daling, “Big Tomb”) relieves the pain of plantar fasciitis. P7 is located in the middle of the transverse crease of the wrist. P7 is a Shu-Stream point and Yuan (Primary) acupuncture point that is known for the treatment of Heart and Spirit related issues including myocarditis, palpitations, insomnia, mental illness, irritability, and cardiac pain. P7 is also used for Stomach related conditions, however, nearby point P6 is a more common point for the treatment of Stomach issues such as stomachache, nausea, and vomiting.
According to Chinese medicine and acupuncture theory, Shu-Stream points treat a heavy sensation of the of the body and painful joints. P7 is therefore a common point for the treatment of wrist pain because it is a Shu-Stream point located at the wrist . However, the researchers have chosen P7 for the wrist’s distal relationship to the ankle and heel region. At a six month follow-up examination, the P7 acupuncture group showed a significant improvement over the control group.
Plantar fasciitis affects approximately 2 million US citizens annually. These findings demonstrate that acupuncture is an important treatment modality for inflammation of the connective tissue on the bottom of the foot. Advantages to acupuncture treatment are that it is both safe, acupuncture is nontoxic and is nonsurgical, and effective.
References:
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, An International Journal of Comparative Medicine East and West. Efficacy of Electro-Acupuncture in Chronic Plantar Fasciitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Wipoo Kumnerddee and Nitsara Pattapong. Volume 40, Issue 06, 2012.
Shi Ping Zhang, Tsui-Pik Yip, and Qiu-Shi Li. Acupuncture Treatment for Plantar Fasciitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial with Six Months Follow-Up. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative, Medicine, Volume 2011 (2011), Article ID 154108.
Acupunct Med. doi:10.1136/acupmed-2012-010183. The effectiveness of acupuncture for plantar heel pain: a systematic review. Richard James Clark, Maria Tighe.\
Link: http://www.healthcmi.com/index.php/acupuncturist-news-online/661-acupunctureceusplantarfasciitisea
No comments:
Post a Comment